Create a client
How to create and manage access to OpenCRVS' interoperability functionality
In order to interoperate with OpenCRVS, you must first create an official client.
Only a National System Administrator role can create a client. E.G. In our example for our fake country Farajaland, this is the user: j.campbell
Login to OpenCRVS as the user: j.campbell
Use the left navigation to select the Configuration > Integrations section.
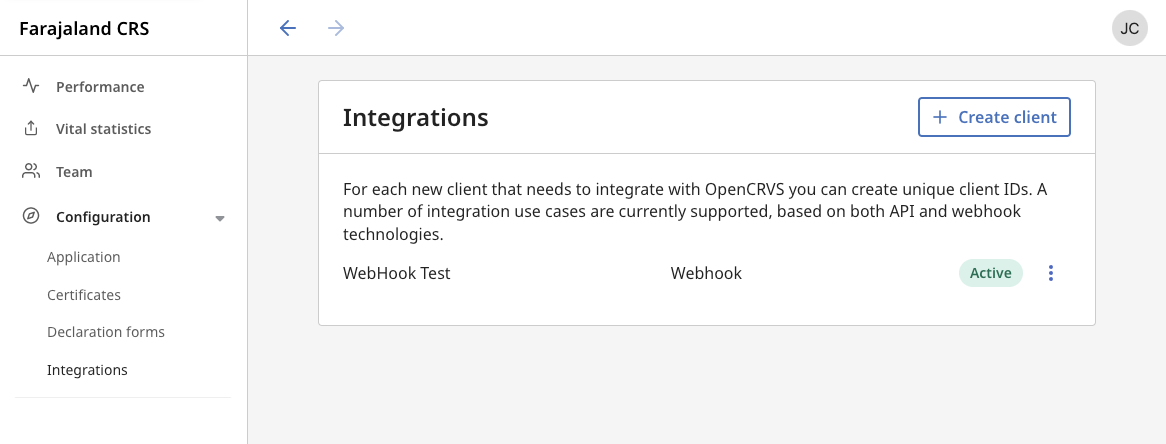
3. Click + Create client
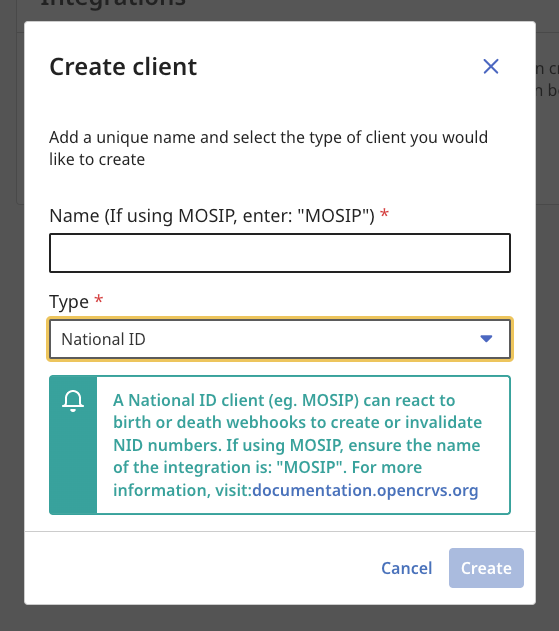
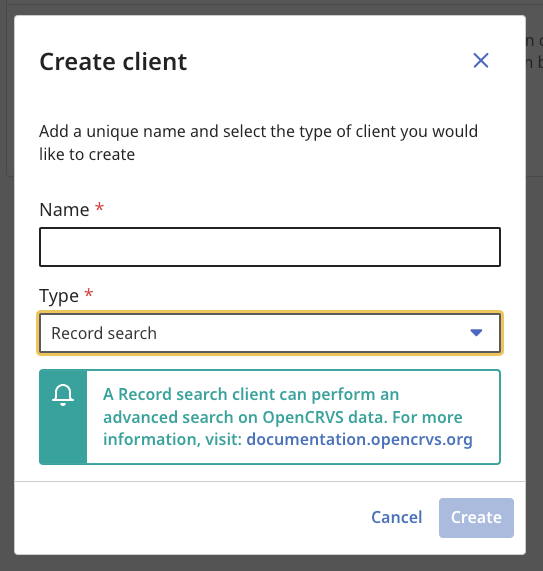
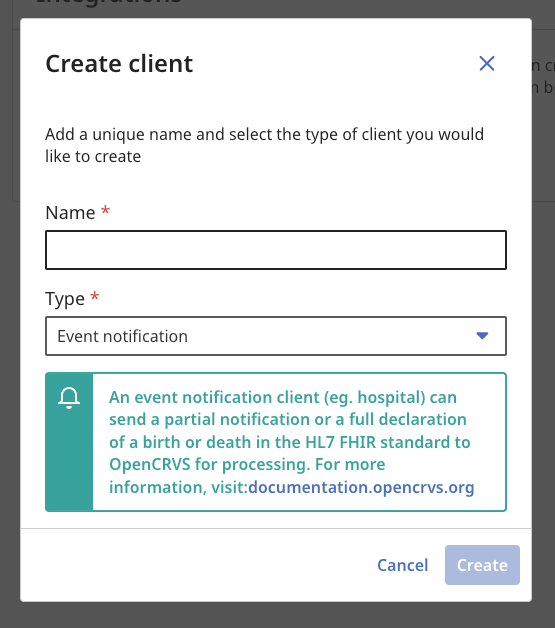
4. You will see a modal overlay where you can select the type of client you wish to create. The business functionality available for each client is explained in subsequent pages in this section of our documentation.
The type of client you create is important and can only perform API requests associated with the business functionality relevant to that type. A Record Search client is not authorized to perform an Event Notification for example.
You must give each client a unique name.
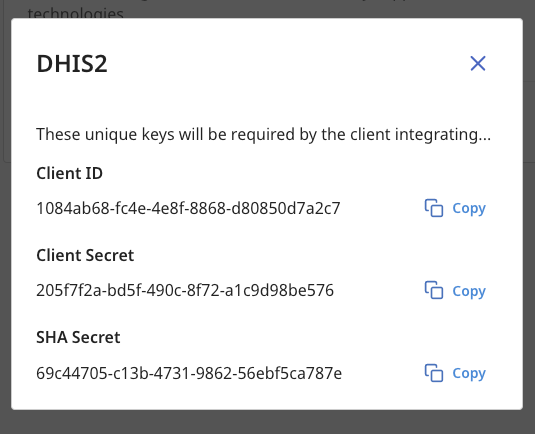
5. When you click "Create", you will be shown the authentication details for the client along with a SHA Secret used to sign, encrypt, decrypt and verify the authenticity of payloads.
You must copy these keys now! The Client Secret will never be displayed to you again and it cannot be retrieved from our database as it is encrypted.
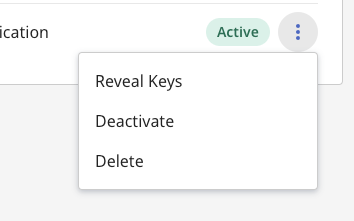
6. You can manage existing clients by using the 3 dots menu after the client has been created. You can reveal the Client ID and SHA Secret keys at any time and refresh the Client Secret to create a new one by selecting "Reveal Keys".
When you refresh a Client Secret, the old secret will no longer work for authentication.
You can also temporarily "Deactivate" and "Enable" a client or alternatively "Delete" it.
All client behaviour is audited and is ultimately the personal responsibility of the National System Administrator of OpenCRVS that created the client. Protect citizen data and do not expose access unnecessarily, as you may be in breach of local privacy laws.